Introduction:
In today’s digital world, safeguarding and keeping your data secure has become more important than ever. One essential tool people use to achieve this is a Virtual Private Network (VPN). With numerous cyber threats and attacks becoming more common, a VPN can be a powerful tool. Whether you are browsing on a public Wi-Fi at a coffee shop or working from home, a VPN helps secure and encrypt connections between your device and the internet.
The VPN not only masks your online activities from prying eyes but also lets you access content that might be restricted in your region.
What is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technological service that reroutes your internet connection through a private server rather than your main internet service Provider (ISP), thereby creating a secure and encrypted tunnel between your device and the internet.
Let’s break down some key points:
- Encryption: VPN’s encrypt your data, making it nearly invincible to hackers, advertisers, or even your internet service providers to snoop on your online activities.
- IP Masking: By connecting to a VPN server, your device appears to have the IP address of that server, which can provide anonymity and help bypass region-specific restrictions.
- Secure Connection: Most useful on unsecured public Wi-Fi networks, a VPN secures your connection and protects sensitive information like passwords, bank credentials, and personal emails.
How Does a VPN Work?
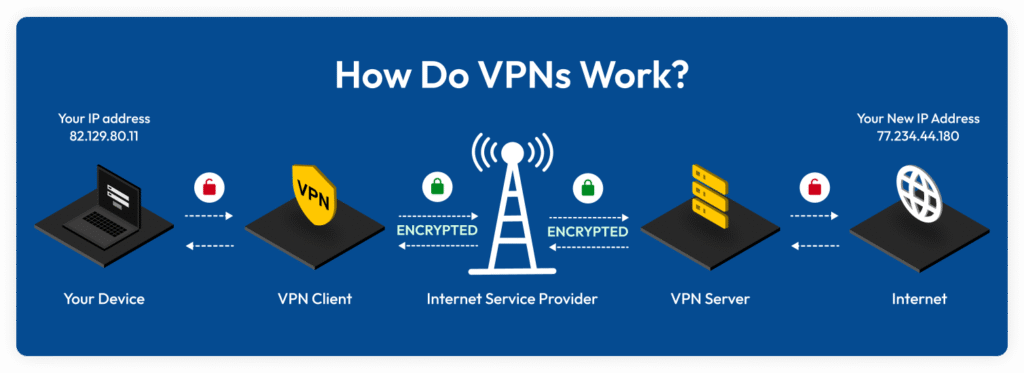
This is what happens when you connect to a VPN server:
- Connection to a VPN server: After successfully installing a VPN software, it automatically connects your device to a server in a location of your choosing.
- Data Encryption: All your data is encrypted before it even leaves your device. This means that even if someone intercepts your data, it won’t be readable.
- Data Transmission: Your data travels securely through this encrypted tunnel to the VPN server and then to its final destination on the internet.
- IP Address Replacement: The website or online service you access sees the IP address the VPN has provided to you, not your actual IP, thus keeping you anonymous.
Why and When You Should Use a VPN
Knowing and understanding the benefits of a VPN can help you decide when it’s a good idea to use one. We have listed the Whys and Whens below.
- Public Wi-Fi Security: Public Wi-Fi networks (like those in airports, cafes, or hotels) are often unencrypted, making it much easier for attackers to intercept your data. A VPN ensures that your connection remains secure, even on these networks.
- Enhanced Privacy: If you’re concerned about your internet service provider tracking your online activities, a VPN can help hide your browsing history. This is also useful if you simply want to keep your online activities private from the government.
- Bypassing Geo-restrictions: Many streaming services and websites restrict content based on your geographic location. A VPN allows you to connect to servers in different countries, enabling you to access content as if you were in those regions.
- Avoiding Censorship: In some countries, access to certain websites or services may be restricted. A VPN can help bypass these blocks, providing you with unrestricted access to the global internet.
Pros of a VPN:
- Strong privacy and security
- Unlock region-blocked websites
- Protects you on Public Wi-Fi
Cons of a VPN:
- May cause a slow internet
- expensive to set up a good VPN


Outstanding story there. What occurred after?
Thanks!